If you want to invest in a business that runs without high volatility and risk, stablecoins offer a gateway to digital currency investments. Learn how to invest in stablecoins.
Concise Overview
- A stablecoin is pegged to the value of something tangible to reduce volatility
- Stablecoins can be fiat-backed, crypto-backed, or commodity-backed
- Investment in stablecoins is influenced by the volatility of other assets
Introduction
You’ve probably heard of Bitcoin and Ethereum — the two most well-known cryptocurrencies. But what about stablecoins? Stablecoins are a new type of cryptocurrency that aims to solve one of the biggest problems with traditional cryptocurrencies: volatility.
While most people think of cryptocurrency as a way to make money, it’s just a representation of value digitally transferable. And the value of these currencies can fluctuate wildly depending on market conditions, hence the need for stablecoins.
But what exactly are stablecoins? How do they work? And why is there so much excitement surrounding them? This piece answers these questions and more.
Definition: What Are Stablecoins?
A stablecoin is a cryptocurrency often pegged to one or more fiat currencies, such as the US dollar. Stablecoins are often used as trading pairs on exchanges and can be pegged to assets and commodities.

The first stablecoin was created in 2014, and today there are many alternatives on the market. These coins are still in their infancy, but they have begun to make waves in the financial world. The most popular stablecoin is Tether (USDT), which has achieved over $60 billion in market cap today.
Why Do You Need Stablecoins?
Investors hold stablecoins to bring the stability of a fiat currency to the crypto world. Being hybrid, the coins can be subject to the three macroeconomic motives for holding money such as:
Transactional
A stablecoin is a cryptocurrency with a fixed price. This means the currency’s value doesn’t fluctuate, making it ideal for purchasing goods and services.
You can use stablecoins for any number of purposes, but they’re often used as collateral on decentralised exchanges. Investors also use them in lending agreements between crypto companies.
Precautionary
The value of a stablecoin is dependent on the strength of its underlying assets. Stablecoins are ideal for transacting in an environment with high uncertainty about the future.
In such cases, people buy stablecoins to hedge against potential losses that could happen if their assets depreciate due to external factors. This type of motive is precautionary.
Speculative
Investors use stablecoins to speculate on the price of cryptocurrencies. Stablecoins have a predictable value, which makes it easier for investors to know how much their assets are worth. This is especially useful if you’re looking to buy and sell at the right time or if you want to invest in speculative assets like other cryptocurrencies.
Types of Stablecoins
There are three main types of stablecoins: fiat-backed, crypto-backed, and commodity-backed. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages over the others. However, all three serve an essential purpose in the crypto ecosystem.
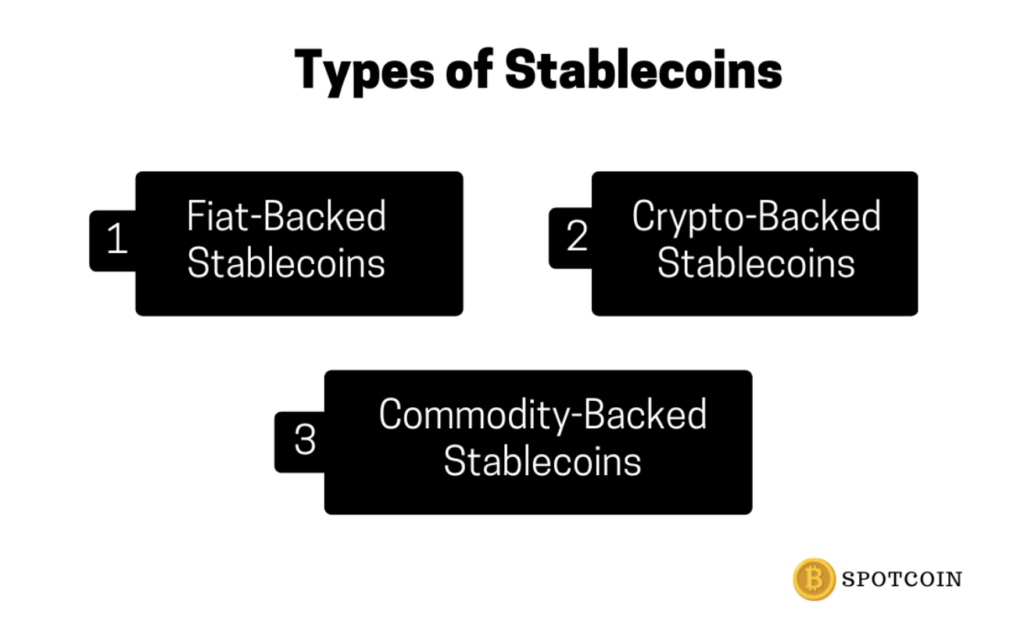
Fiat-Backed Stablecoins
Fiat-backed stablecoins are backed by fiat currency. In other words, they’re designed to be pegged at a stable rate to an underlying fiat currency (like the US dollar or the euro). The most common method is through a collateralised reserve system, where tokens are fully backed by cash reserves held in a bank account. An example is USD Coin (USDC).
Crypto-Backed Stablecoins
A cryptocurrency backs crypto-backed stablecoins — for example, Bitcoin or Ethereum. They’re typically issued on top of decentralised blockchains like Ethereum. This means they’re programmable and have smart contracts, which can be used to keep track of the funds backing the coins in circulation. An example is Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC).
Commodity-Backed Stablecoins
Commodity-backed stablecoins are those backed by physical commodities. These assets can be anything from gold and silver to oil, copper, and other metals and minerals. This type of crypto coin contains an underlying asset held in escrow by a third party who vaults it securely until it’s needed for redemption. An example is Paxos Gold (PAXG).
Are Stablecoins Cryptocurrency?
There are arguments that stablecoins are not perfect cryptocurrencies. To understand how much cryptocurrency is a stablecoin, there’s a need to see if it meets the standard features of an average cryptocurrency. Below is a comparative assessment:
| Features | Cryptocurrencies | Stablecoins |
| Intangibility | Intangible | Intangible |
| Decentralisation | Fully decentralised | Not fully decentralised |
| Limited Supply | Theoretically limited | Practically limited |
| Peer-to-Peer | Fully peer-to-peer | Not fully peer-to-peer |
| Open Source | Fully open-source | Not fully open-source |
Intangibility
Stablecoins are not tangible and cannot be physically held in your hands. The value of a stablecoin is determined by its price in other assets, which means it doesn’t exist as an actual object in the real world. Although intangible, some stablecoins offer tangible value (such as fiat-backed).
Cryptocurrencies are also intangible and can’t be held physically. Cryptocurrencies also hold no real-world value because they’re purely digital assets that lack physical representations like dollars or gold.
Decentralisation
In the case of cryptocurrencies, they’re entirely decentralised. There’s no central authority or third party involved in validating transactions or maintaining records. However, some stablecoins are centralised (fiat-backed), such as Tether, while others are decentralised (crypto-backed), such as DAI.
Limited Supply
Cryptocurrency being limited in supply means it should never have more than 21 million coins (Bitcoin theoretically doesn’t). The supply of most cryptocurrencies is practically unlimited, and they can be created at will by mining. Stablecoins are different because they’re designed to hold a particular value over time.
To maintain their price, some stablecoins must be destroyed (burned) when they change owners. Stablecoins also use bank reserves or other assets as collateral against which users can borrow (or lend) funds so that no new coins need to be created for these purposes (pegging).
Peer-to-Peer
A peer-to-peer (or P2P) network is a decentralised network that connects nodes directly. It allows the transfer of data or information between two or more computers without an intermediary, such as a central server.
Decentralised stablecoins are essentially peer-to-peer. This means there’s no intermediary or third party involved in transactions. They adopt blockchain technology to ensure the security, transparency, and immutability of digital currencies.
Open Source
Open source software is software that has its source code made available and licensed such that anyone can study, modify, improve, and reuse it. This software is often developed in a public collaborative manner.
In the crypto world, this means blockchain-based stablecoins are not only decentralised but also share their code with the general public. That way, everyone can use it. In theory, this makes them more secure because bugs will be found faster and fixed quicker.
Are Stablecoins CBDCs?
Stablecoins are not CBDCs. Stablecoins are digital currencies designed to maintain a stable price as a store of value. CBDCs are also digital currencies, but they serve a different purpose than stablecoins do.
The term ‘Central Bank Digital Currency’ refers specifically to traditional fiat currencies (like USD) digitised by central banks. In other words, if you hold an account at your bank and want to deposit $50 into it using the bank’s mobile app or website, that money will exist in digital form on the bank’s servers rather than be printed out on paper dollars.
Because CBDCs aren’t meant for storing value like stablecoin—they’re meant for spending—they don’t need any fiat or gold backing. So long as everyone agrees these digital tokens have value based on their trustworthiness, they’ll function just fine.
What Are the Risks of Stablecoins?
When stablecoins first came out, everyone was pretty excited about them. Not only were they a new kind of cryptocurrency, but they also promised to solve one of the biggest problems with cryptocurrencies: volatility.

But as interest in stablecoins has grown, so have concerns over their risks. While plenty of benefits come with using a stablecoin, some potential downsides are worth keeping in mind.
Fluctuation
Even though most stablecoins are meant to maintain a relatively fixed price, their market value isn’t guaranteed by any authority like central banks or governments. Therefore, the value can change based on factors such as supply and demand.
In particular, when demand increases for a given stablecoin, its price will increase until supply meets demand and stabilises again at its target value (assuming there isn’t too large of an imbalance). This process can happen very quickly if there’s enough interest in buying the coin at once, resulting in fluctuations.
One infamous example was how investors flooded to exchange their Tethers for dollars a few months ago. Cryptocurrencies plummeted, and panic set in. This resulted in USDT dropping below $1 within hours despite being intended as an ultra-stable asset worth exactly $1 each unit.
Manipulation
Stablecoins are meant to be used as a store of value, but they can be manipulated in many ways. And because stablecoins are new and there’s no precedent for them yet, there’s no way to know what kinds of protections buyers need to avoid the manipulation.
For example, if a stablecoin is backed by a physical asset like gold or silver, it will only hold its value as long as those assets are available and not being drained by other people taking them out of circulation. If someone has access to more gold than they should, they could sell it all on the market at once and crash the price of that stablecoin—and potentially even other cryptocurrencies that depend on it for stability.
Regulation
Stablecoins aren’t yet widely regulated, but as they grow more popular, regulators have begun to take notice. In the United States alone, several regulations have been proposed or enacted already. Blackfridge just issued the first regulated British Pound stablecoin, known as Poundtoken (GBPT).
These regulations can be positive and negative, depending on who you ask. For example, many investors favour stablecoins and oppose government intervention in the system. But others consider this necessary, so consumers know what they’re getting into before buying something or investing.
Steps to Safely Buy Stablecoins
Stablecoins are the latest craze in crypto investment. They’re a sort of bridge between traditional fiat currency and digital assets. But to buy them isn’t an easy process. Here are steps to guide you:
Decide Which Stablecoin to Buy
One of the most important things to do when investing in stablecoins is to research the coins you want to buy and ensure they’re legitimate. If you want a stablecoin backed by fiat currency, look for one an independent third party has audited.
Look at the fundamentals. Check out their whitepapers and other documents on their websites or in their Github repositories. You should see how many tokens have been minted so far and how many remain unmined. Doing this helps inform your investment decisions.
Pick a Secure Crypto Exchange
It’s essential to look for crypto exchanges that have a good reputation, are regulated, trustworthy, and have a track record. You can do this by checking out the exchange reviews you’re looking at. Many websites can help you with this.
These review sites usually don’t just report on whether or not an exchange has frozen your account or stolen money from other users but also how reliable they’re. You should also double-check the exchange’s terms of service to ensure they don’t charge hidden fees or withhold vital information from customers.
Make an Account
You need to create an account with the exchange where you want to purchase your coins. You must provide your name, email address, and contact information (including phone number).
You should ensure the username and password are firm and not easily guessed by others. Also, choose a unique email address that only you use on all of your accounts.
You’ll also want to ensure the phone number associated with the account has been secured by two-factor authentication (2FA). If possible, try to add an extra layer of security by setting up a Google Authenticator app or similar application for added protection.
Buy the Stablecoin
To buy stablecoins, you’ll need first to purchase crypto and then use your crypto to buy stablecoins. This will require a self-custody wallet. Self-custody wallets are secure and private wallets that hold funds on behalf of users. They’re usually provided by a third party and require users to enter a passcode or biometric identifier to access their funds.
Tips for Investing in Stablecoins
Stablecoins are great for investing because they’re relatively safe compared to volatile cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. But that doesn’t mean they’re immune from risk altogether. Several stablecoin projects have failed over the years due to technical issues or regulatory setbacks, and there’s still no guarantee that all stablecoins will survive long term.

That said, here are tips to keep in mind when investing in stablecoins:
Understand Your Coins
Before investing in stablecoins, you should understand how the coins work. You should choose which type of stablecoin to invest in and understand how it works. If its price is too volatile compared with its target rate (for example: if it’s below $1), some risks may be involved.
Avoid Volatility
It’s important to note that you should avoid trading during volatile periods. This means avoiding purchasing stablecoins when the market is going through a downturn. It’s even more necessary if your goal is to purchase them as a long-term investment.
Erase Your Losses
One of the best things about stablecoins is they can provide investors with a ‘reset’ button regarding their portfolios. If you’re not happy with the way your portfolio is performing, or if you think there are better opportunities elsewhere, consider liquidating some of your holdings to create room for other investments.
Diversify Your Portfolio
The final tip is to diversify your portfolio. Don’t put all your eggs in one basket — and don’t invest more than you can afford to lose. If you’re looking at stablecoins as an investment opportunity, it’s best to do so with the same approach as any other type of coin: only invest what you can afford not to lose.
Investing in Stablecoins: The Bottom Line
There are more reasons to use stablecoins than there are to use traditional currencies, and they’re a great way to diversify your portfolio. While they won’t replace fiat cash or cryptocurrencies, they could provide a haven in times of economic crisis or political turmoil.
The most significant advantage of investing in stablecoins is that you don’t have to worry about losing value due to inflation or deflation. As long as the cryptocurrency market remains strong, these coins will remain valuable assets.